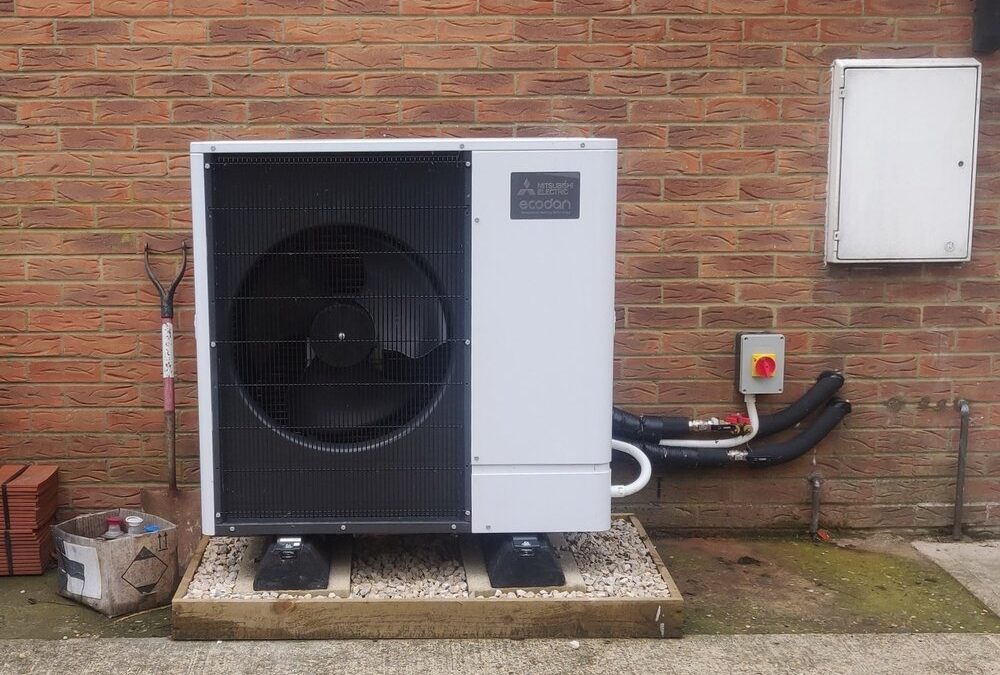
Air source heat pumps (ASHPs) are a beacon of energy efficiency and environmental friendliness in the realm of heating and cooling solutions. However, acknowledging their disadvantages is crucial for a well-rounded understanding. Truth be told, when air source heat pumps are designed and fitted with precision, their advantages can significantly overshadow these limitations, offering a sustainable and efficient alternative to conventional systems.
Navigating the Initial Investment
The upfront cost associated with ASHPs often stands out as a primary concern. The price tag, influenced by the system’s size and the complexity of installation, might initially seem daunting. Yet, this initial investment paves the way for substantial energy bill reductions in the long run, positioning ASHPs as a financially sound choice over time.
Weather-Dependent Efficiency
ASHPs are known to face efficiency challenges in extreme cold, with their ability to extract heat from the air diminishing as temperatures drop below freezing. This can lead to increased operational costs during the coldest months. However, modern advancements in ASHP technology have expanded their operational range, ensuring they remain a viable heating source in temperatures as low as -15°C, albeit with slightly reduced efficiency.
Sound and Sight: Modern Improvements
Earlier ASHP models were criticized for their noise and the potential aesthetic impact of the outdoor unit. Technological strides have since mitigated these issues, with current models boasting noise levels comparable to a domestic refrigerator and designs that blend more seamlessly into residential settings.
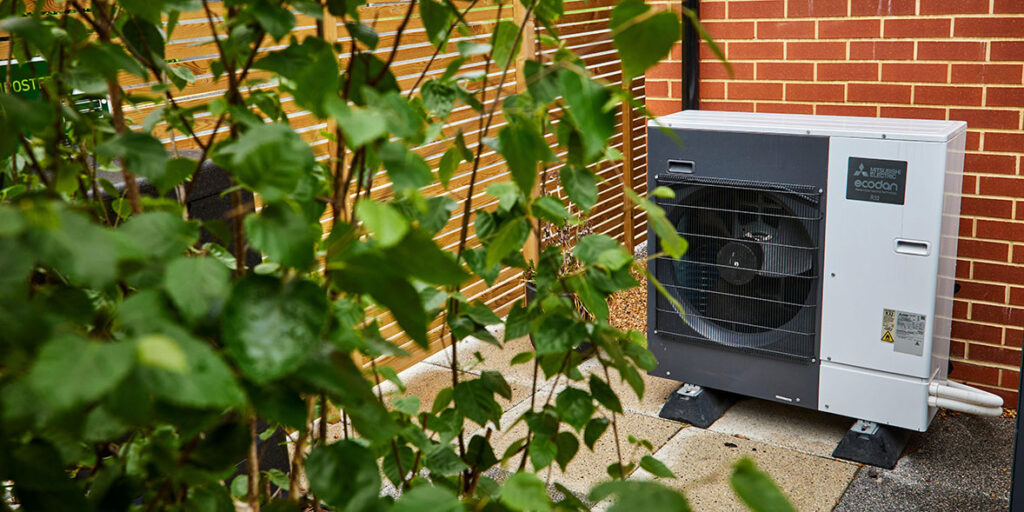

Electricity: A Double-Edged Sword
ASHPs’ reliance on electricity is a double-edged sword; it ties their environmental impact to the source of the electricity used. In regions where the grid is powered by renewable energy, ASHPs enhance a home’s green credentials. Yet, during power outages, this reliance can be a notable drawback.
Lifespan and Maintenance: The Path to Longevity
With a typical lifespan of around 15 years, ASHPs may require replacement sooner than some traditional heating systems. Regular maintenance is key to extending their life and ensuring consistent performance, emphasizing the importance of ongoing care.
In Conclusion
Despite these considerations, the virtues of air source heat pumps, particularly when expertly designed and installed, cannot be overstated. Their ability to reduce carbon emissions and operate on renewable electricity makes them a cornerstone of sustainable living. The key lies in professional installation and choosing a system tailored to the specific needs and climate of the area, ensuring that the benefits of ASHPs are fully realized.
In essence, while air source heat pumps come with certain disadvantages, their capacity for energy savings and environmental conservation marks them as a forward-thinking choice in home heating and cooling. By addressing these drawbacks through informed decision-making and professional guidance, homeowners can harness the full potential of ASHPs, making them a compelling component of modern, eco-friendly living spaces.